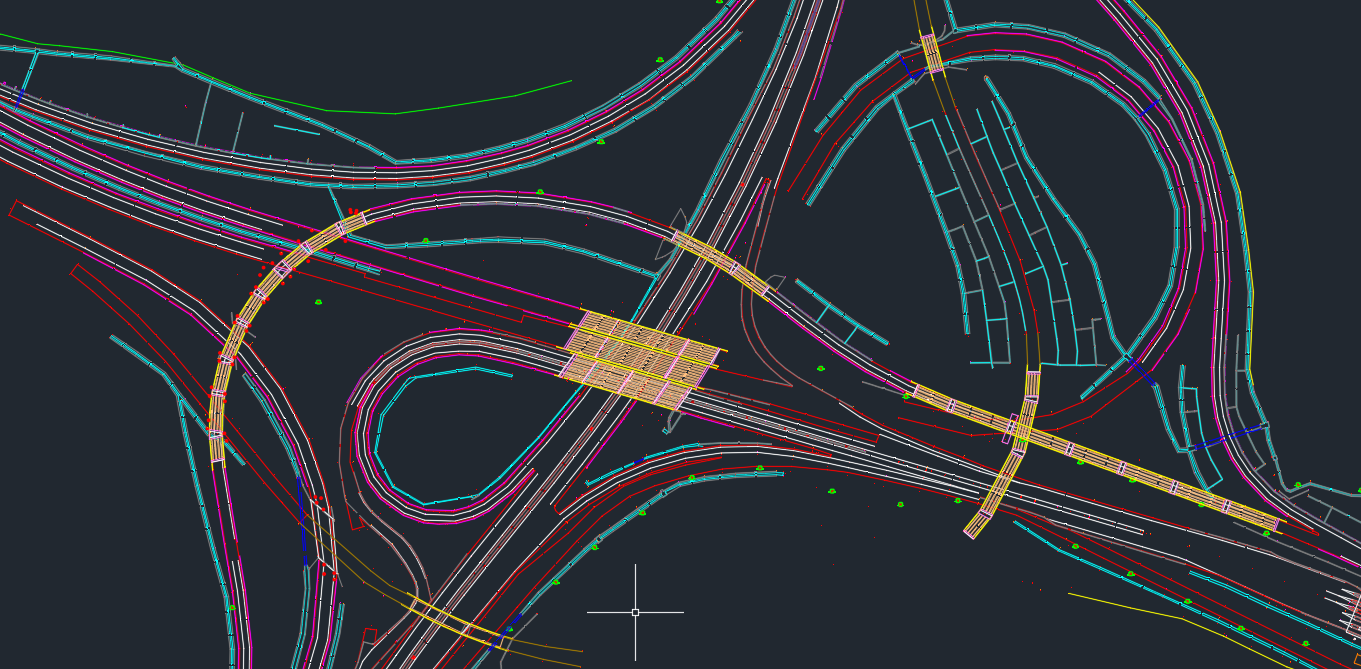
Topography Survey
Problem We Solve
In the development planning process, layout designs often do not fully consider the real conditions on the ground. This can lead to various problems, such as incorrect placement of buildings or access points, inaccurate soil cut and fill calculations, and inappropriate drainage systems that cause water runoff. These mismatches not only impact cost and time efficiency, but also risk environmental damage and disruption to building structures in the future.
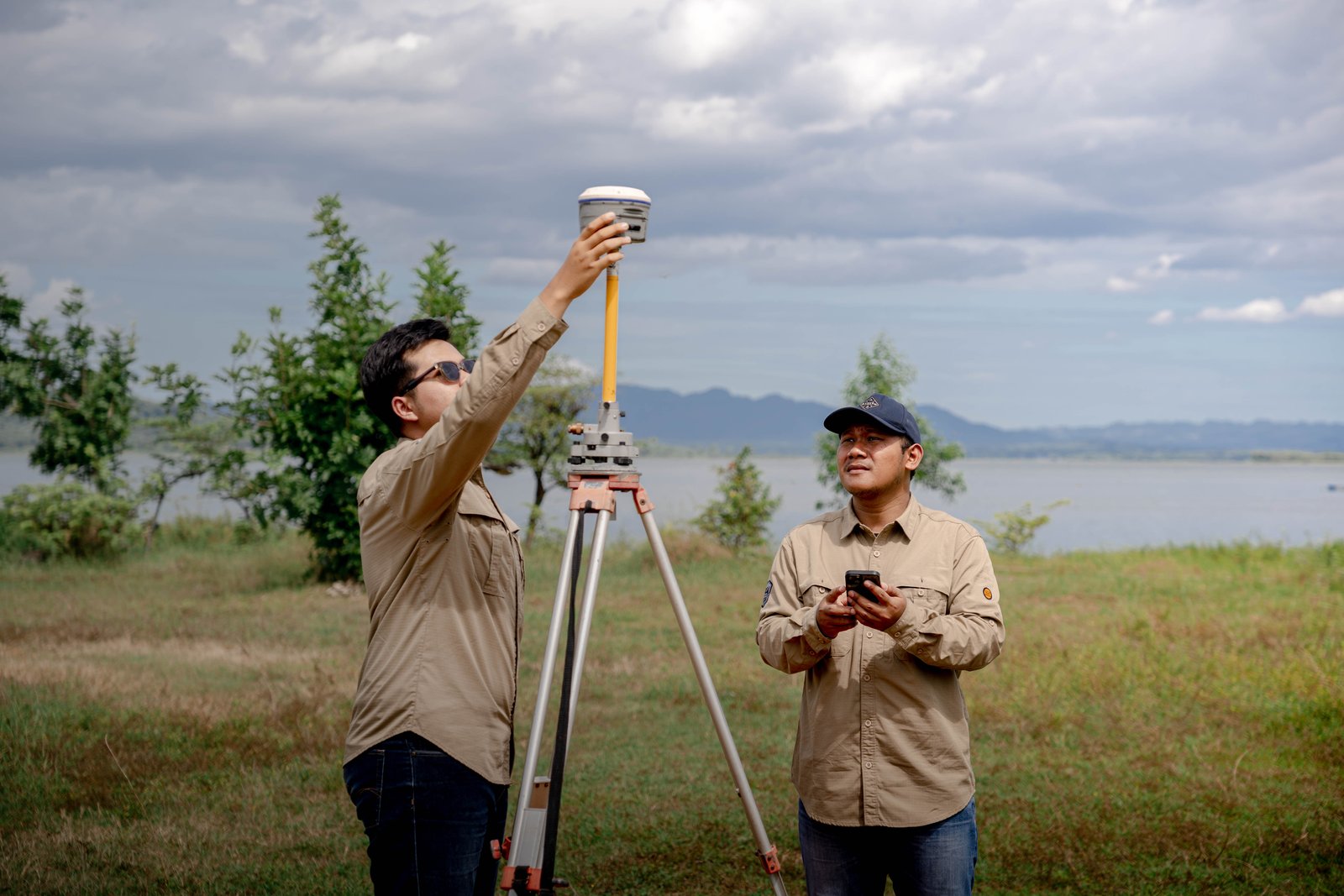
To address this, terrestrial topographic surveys are an important step that should not be overlooked. These surveys are conducted directly from the ground using tools such as total stations, geodetic GPS, or laser scanners, and are capable of producing data with an accuracy of up to 2 mm-a level of precision that aerial surveys struggle to achieve. With precise topographic information, the planning and construction process can be carried out more precisely, efficiently, and in accordance with the actual conditions of the project site.
How Our Topographic/Terrestrial Surveying Empowers Your Projects
We combine Total Station, GNSS, and Automatic Levels to ensure you get the most reliable geospatial data:
-
1. Terrestrial Laser Scanner (TLS): This advanced device captures millions of data points rapidly, creating a highly detailed 3D "point cloud" of your site. It's ideal for complex structures, intricate environments, and areas where extreme detail is needed. This method allows for direct extraction of highly accurate 2D or 3D topographic information.
-
2. Total Station (TS): This electronic instrument gathers highly detailed point coordinate data with millimeter accuracy, perfect for structures, boundaries, and obstructed areas.
-
3. Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS): Using satellite signals (like GPS), GNSS quickly and accurately determines positions in large open areas, crucial for establishing your project's main control network.
-
4. Automatic Level: This optical tool is essential for establishing precise horizontal planes and measuring elevation differences, ensuring everything from foundations to slopes is perfectly level.
The Incredible Benefits You’ll Gain
Superior Accuracy
Highly precise data reduces planning errors and ensures reliable execution.
Field Time Efficiency
Integrated TS, GNSS, and Levels accelerate data collection and verification.
Smarter Decisions
Accurate geospatial data supports better planning and coordination.
Lower Costs
Early issue detection reduces rework and prevents budget overruns.
Topographic Survey Flow
Point Control Survey
Survey to determine geodetic reference points in the field
Topography Survey
Terrain data collection (elevation and physical features of the ground surface)
Processing Contour and Situation Result
Processing survey results into digital using CAD or GIS software
DTM and Site Plan Creation
Create digital model and site plan