In the modern construction and architecture industry, Scan to BIM technology has become a highly effective solution for improving efficiency in building design, planning, and management. This technology transforms traditional methods of building modeling by relying on scanned data to produce accurate digital representations.
What Is Scan to BIM?
Scan to BIM is the process of scanning a physical object such as a building or structure into an accurate digital model. Scanning uses accurate technology, such as a laser scanner. The laser scanner will scan the object by emitting laser pulses to the object to obtain a set of point clouds that form a 3-dimensional model. The point cloud data is processed such as merging and removing unnecessary noise. The processed point cloud data is used as the basis for creating a BIM model according to the desired LOD.
Benefits of Scan to BIM
-
High Accuracy
The scan data provides a highly accurate representation. The data includes details of the scanned area and MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) structures.
-
Time and Cost Efficiency
The field data collection process is faster, reducing the need for manual surveys. Scan to BIM can also minimize project errors. Time efficiency has an impact on project cost efficiency.
-
Ease in Renovation and Restoration
Scan to BIM is useful in rehabilitation projects of old or heritage buildings with clearer existing condition data.
-
Data Asset Management
Scan to BIM can create detailed technical documentation and help the asset maintenance process.
-
Better Collaboration
BIM models allow different parties, such as architects, engineers, and contractors, to work with the same data in one platform.
Final Product 3D Modeling Using Scan to BIM Method
-
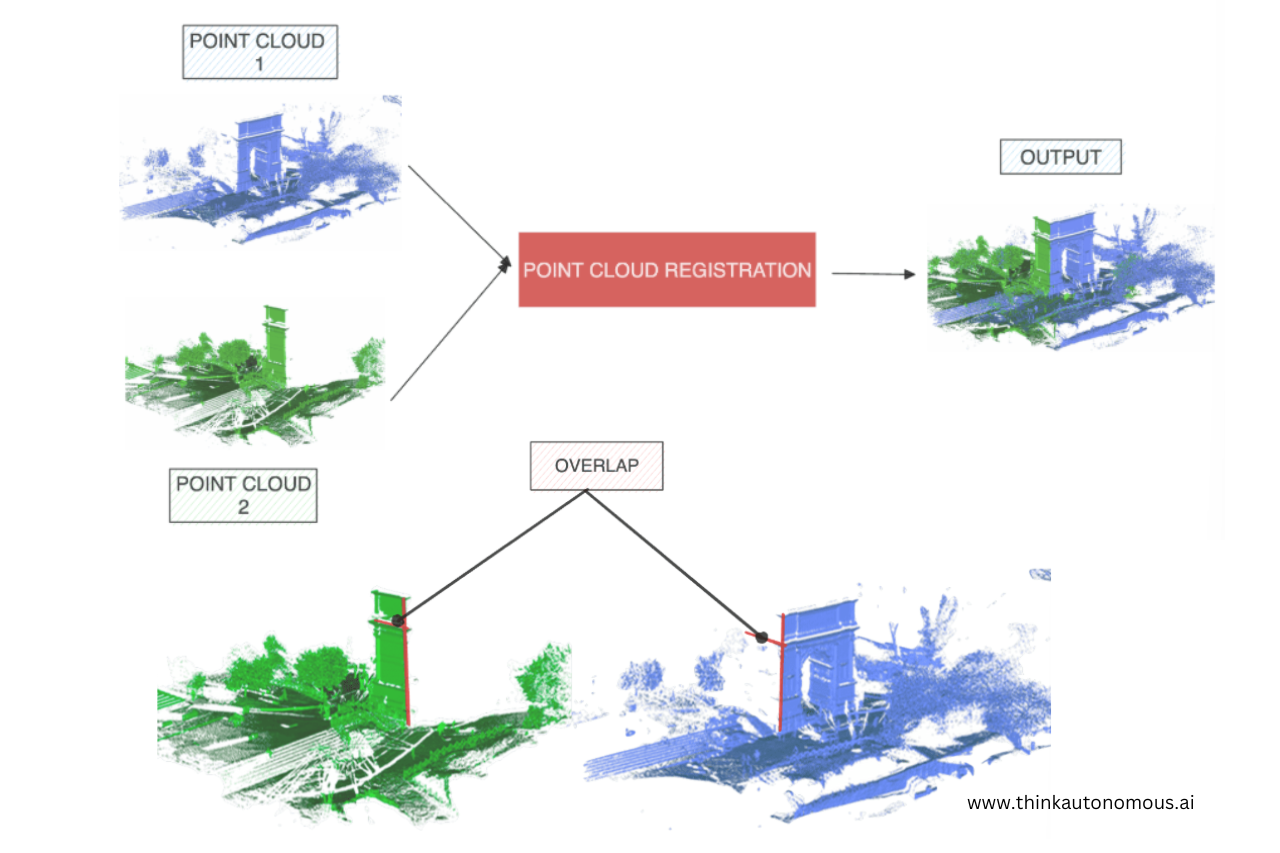
Register Point Cloud: the result of merging point clouds from various separate data captures.
-
3D Model: a digital representation of a physical object in the real world.
-
Mesh and Contour: Detailed surface representation of the scan results that are useful for analyzing the shape and topography of the building.
-
Video Walkthrough: An interactive visual simulation that allows users to virtually explore a 3D model, particularly useful in project presentations and design evaluations.
Conclusion
Scan to BIM has revolutionized the way the construction and architecture industries handle building data. With the combination of scanning and BIM technology, projects can be done more efficiently, accurately and cost-effectively. As technology develops, the application of Scan to BIM in the future is predicted to become more widespread, supporting the concept of digital twin in the modern construction industry.

.png)